Detect violations of coding rules presented in test specifications
Test area
software
Software functional safety testing

Potential risks due to system malfunction
It is an essential verification process to prevent and ensure user safety.
This is a test to evaluate the safety of a system by evaluating whether the safety system, which integrates hardware and software as required by the standard, has achieved functional safety.
Scope and test specifications
Electrical Appliance Safety Standards for Industrial Lithium Secondary Batteries
- This Act regulates the safety and environmental testing methods for lithium secondary cells and batteries used in energy storage systems (ESSs), as well as the corresponding requirements.
- Software testing is covered in Annex E.
Software for medical devices and medical devices with embedded software
- Electrical Appliances Safety Defines lifecycle requirements for medical device software development.
- Applicable to the development and maintenance of standalone medical software and embedded medical device software.
automatic control device
IEC 60730-1 Automatic electrical controls
- It applies to automatic control devices used in or in combination with equipment for household and similar purposes, including control devices for heating, air conditioning, and similar purposes.
- This equipment can be powered by electricity, gas, oil, solid fuel, or solar energy, either alone or in combination. Software testing is covered in Appendix H.
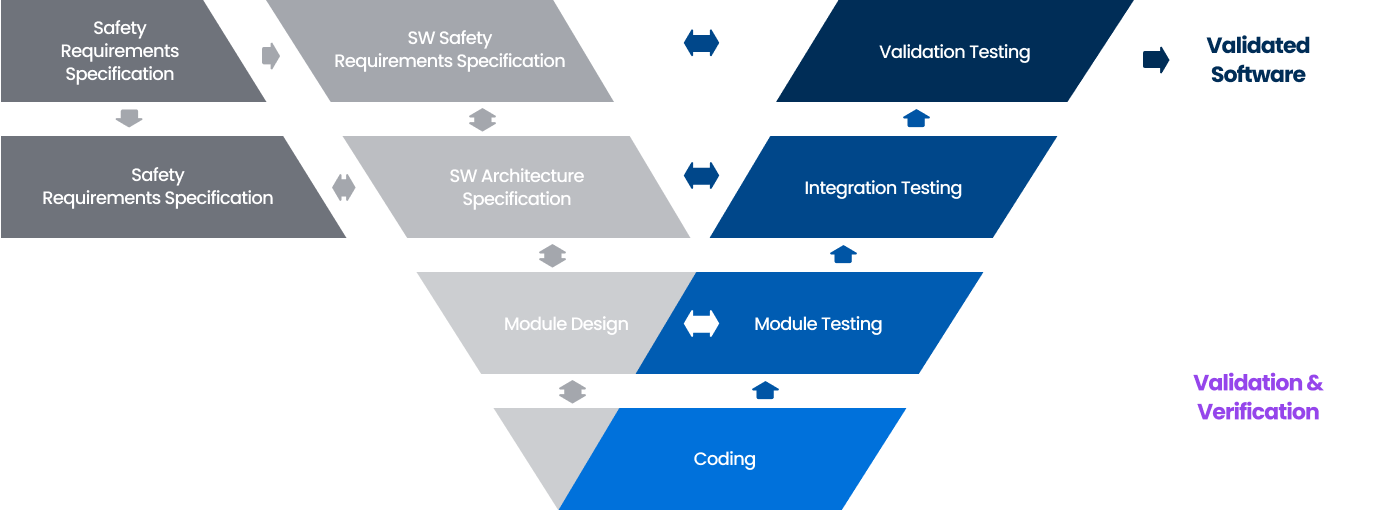
Software Verification Model V&V
A SW quality verification model that verifies the SW development stage according to user requirements and confirms whether the developed SW meets user requirements.
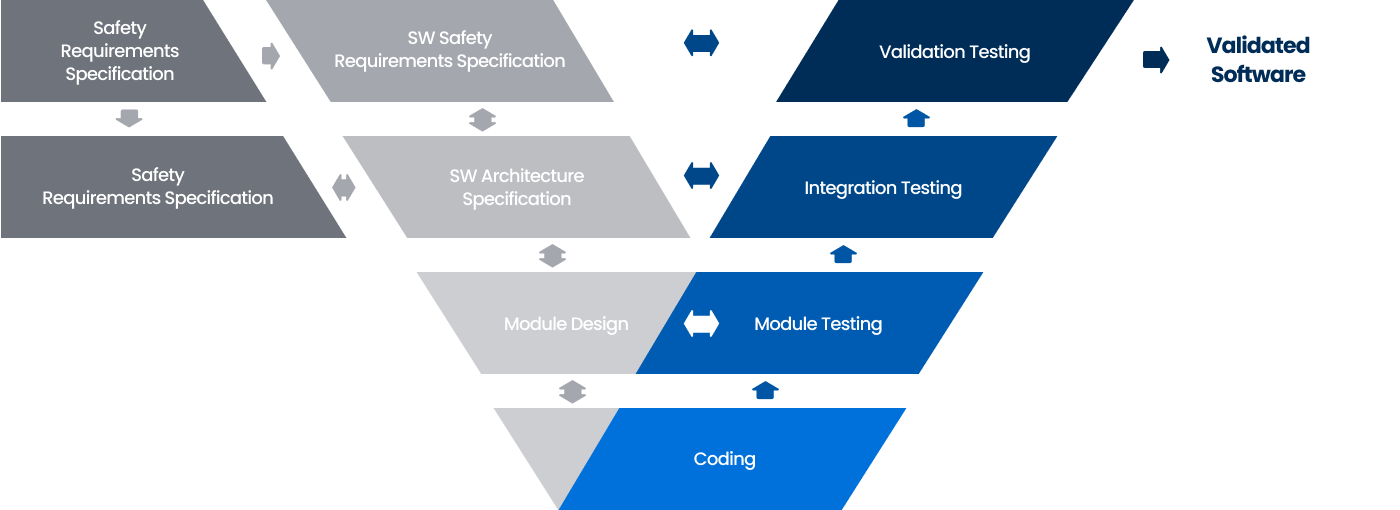
Software Testing Procedures
application

counsel

receipt

test

Issuance of test results
Required documents: Test request application, test agreement, functional safety documents (safety concept document, safety analysis report, test report, etc.)
Software static testing

By verifying every line of code according to coding standards,
Ensures the quality and integrity of the software.
This test ensures software reliability and improves quality by verifying that it meets the static analysis (design and coding standards) criteria for functional safety.
Scope and test specifications
Test criteria
Static analysis applying standards/specifications according to customer requirements
Test procedure
receipt

counsel

Payment of fees

Test execution

Issuance of test results
Required documents: Test request application, test agreement
Software R&D project verification test

Successful results of R&D projects,
Through objective testing by an accredited testing agency
It officially proves its reliability and value.
This testing service provides quantitative evaluations of the results of national and public institution R&D projects through third-party testing, ensuring reliability and verifying objectivity. We conduct testing using the testing methods proposed by the requesting company against the development and performance indicators specified in the business plan and project plan, and issue an official test report.
- Applicable target and
Test specifications -
01 National/public institution R&D project results02 IT products in all fields of SW∙ICTAll fields of software and ICT
R&D project results
web application
Mobile
embedded
Package SW
Other SW
- Test criteria
-
Point 01
Development and performance indicators specified in the business plan and project plan
Point 02Test method presented by the testing company
Software Quality Testing

Objective based on international standards (ISO/IEC)
By evaluating the quality and competitiveness of software,
I prove it.
This test, based on international standards ISO/IEC 25023 and ISO/IEC 25051, aims to ensure the competitiveness and reliability of customers' software products. It objectively evaluates software products based on quality characteristics such as functional suitability, performance efficiency, compatibility, usability, reliability, security, maintainability, and portability.
- Applicable target and
Test specifications -
- ISO/IEC 25023
- International Standard for Software Product Quality Requirements and Assessment
- ISO/IEC 25051
- International Standard for Software Product Quality Requirements and Testing

- System/Software Product Quality
- Functional suitability
- Functional completeness
- Functional accuracy
- Functional adequacy
- Performance efficiency
- Time responsiveness
- Resource efficiency
- Capacitive
- Compatibility
- coexistence
- Interoperability
- Usability
- Appropriate recognition
- Learnability
- Operability
- User error prevention
- Interface aesthetics
- Accessibility
- reliability
- Maturity
- Availability
- Fault tolerance
- Recoverability
- Security
- confidentiality
- Integrity
- Non-repudiation
- Responsibility
- Authentication
- Maintainability
- Modularity
- Reusability
- Analytical
- Changeability
- Testability
- Portability
- adaptability
- Installation
- Substitutability
- Test subject
-
All areas of software, including mobile, embedded, digital content, web management tools, home networks, and games.
All areas of softwareweb application
Mobile
embedded
Package SW
Other SW
Test procedure
application

Review and discussion of test standards

receipt

test

Issuance of test results
Documents to be submitted for software R&D project verification testing: Test request application, test agreement
Documents to be submitted for software quality testing: Test request form, test agreement, software product (product manual, user manual, executable software)
IoT Cybersecurity Exam

Trust in a connected world is invisible
It starts with protecting your personal information and networks from cyber threats.
This test evaluates the security of IoT (Internet of Things) devices and verifies personal information protection and network safety.
Applicable target
It establishes common security requirements for all wireless devices connected to the Internet, including smart home and IoT devices, childcare equipment that processes personal information, location, and traffic data, wireless toys, and wearable devices.
And wireless equipment that processes monetary values such as virtual currency and electronic finance
Wireless equipment and intermediate equipment may be included in the test scope.
- Product range
-
+
wireless equipment3G, 4G, 5G, LTE/M, NB-IoT
IP communication
Wi-Fi, BLE
intermediate equipment
IP communication
Internet
+
wireless equipmentChildcare equipment, toys, and wearable devices
(2009/48/EC)

- RED guidelines
-
RED 3.3(d)
Directly or through other equipment
Equipment that can communicate with the InternetRED 3.3(e)Wireless devices capable of processing personal, traffic, and location data
(including childcare equipment, toys, and wearable devices)RED 3.3(f)A product that allows the transfer of digital assets without legal status
(including virtual currency)
Test criteria
A series of standards for cybersecurity assessment of products containing wireless communication functions in accordance with the European Union RED Directive (2014/53/EU).
Common Security Requirements
Defines basic security requirements common to general wireless devices connected to the Internet.
We establish a cybersecurity foundation across our products, including access control, user authentication, security updates, data storage, and communication security.
Security for Data-Processing Radio Equipment
This applies to wireless devices that process personal information, location, and traffic data, particularly childcare equipment, wireless toys, and wearable devices.
Includes privacy-focused security requirements, including personal information protection, basic access control for child users, parental management features, and log/delete functions.
Security for Financial Radio Equipment
It targets wireless devices that are connected to the Internet and process monetary values such as virtual currency or electronic finance.
Addresses security-centric requirements such as multi-factor authentication, financial data encryption, and integrity assurance.
Test procedure
application

Review and discussion of test standards

receipt

test

Issuance of test results
Medical Device Cybersecurity Testing

For patient safety, all medical devices must be cyber-secure.
It is imperative to verify the requirements.
To ensure the safety and security of medical devices, cybersecurity requirements for medical devices are established.
It is a verification test.
Applicable target
Test criteria
Medical Software Lifecycle Security Electrical Appliance Safety Standards
This international standard defines security requirements that must be applied throughout the entire lifecycle of medical software and IT systems, from development through maintenance and disposal.
Medical devices with built-in medical IT network security software
This standard addresses the requirements for medical devices connected to IT networks to safely exchange data from external threats and prevent them from compromising the security of the entire network.
FDA Premarket Cybersecurity Guidance
This is a key regulatory guidance document that outlines the cybersecurity risk management and documentation requirements required by the FDA before medical devices are released to the US market.
IEC TR 60601-4-5 Requirements FR
Identification and Authentication (IAC)
Ability to verify and authenticate identity to ensure that only authorized users can access the system.
Usage Control (UC)
Prevent unauthorized use by controlling accessible data and functions based on user roles and permissions.
System Integrity (SI)
Maintains system integrity by preventing software and data falsification and modification due to malware or hacking.
Data Confidentiality (DC)
Encrypt important data, including patient sensitive information, to protect it from unauthorized access and leakage.
Data Flow Restrictions (RDF)
Control network paths to ensure communication only with authorized servers or other devices;
Preventing information leaks
Timely Event Response (TRE)
Supports real-time detection and recording of security threat events such as hacking attempts, and rapid response.
Resource Availability (RA)
The system is not paralyzed by external attacks and is guaranteed to operate normally whenever needed.
Identification and Authentication (IA)
Ensure that only authorized users have access to the system
Ability to verify and authenticate identity
Usage Control (UC)
Data accessible based on the user's role and permissions
Control functions to prevent unauthorized use
System Integrity (SI)
Protecting software and data from malware and hacking
Maintaining the integrity of the system by preventing forgery and tampering
Data Confidentiality (DC)
Encrypt important data such as patient sensitive information
Securely protected from unauthorized access and leaks
Data Flow Restrictions (RDF)
Control network paths to ensure communication only with authorized servers or other devices;
Preventing information leaks
Timely Event Response (TRE)
Real-time security threat events such as hacking attempts
Support for detection, recording, and rapid response
Resource Availability (RA)
The system is not paralyzed even by external attacks,
Ensures normal operation whenever needed
IEC 81001-5-1 Process Cycle
Test procedure
application

Review and discussion of test standards

receipt

test

Issuance of test results
Domestic medical device cybersecurity testing

In the medical environment of the hyper-connected era, patient trust is
Safety from invisible cyber threats
It starts with guarantees.
Security vulnerabilities of products subject to cybersecurity requirements for medical device approval and review
We conduct tests to objectively evaluate.
Applicable target
Medical devices with wired or wireless communication paths (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, USB, RS-232, LAN, etc.)
Products with embedded software to control medical device hardware or perform specific functions
- Firmware
- Programmable Logic Controller (PLC)
A product that is independent of hardware and is used for medical purposes by itself.
- Medical Image Analysis Software
- Disease diagnosis assistance application
- Treatment Planning Software
Test criteria
Ministry of Food and Drug Safety Medical Device Cybersecurity Requirements Testing and Report Issuance
Medical Device Cybersecurity Permitting and Review Guidelines (Guide for Complainants)
Medical Device Cybersecurity Approval and Review Guidelines
Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS)Identification and Authentication (IA)
Ensure that only authorized users have access to the system
Ability to verify and authenticate identity
Usage Control (UC)
Data accessible based on the user's role and permissions
Control functions to prevent unauthorized use
System Integrity (SI)
Protecting software and data from malware and hacking
Maintaining the integrity of the system by preventing forgery and tampering
Data Confidentiality (DC)
Encrypt important data such as patient sensitive information
Securely protected from unauthorized access and leaks
Timely Event Response (TRE)
Real-time security threat events such as hacking attempts
Support for detection, recording, and rapid response
Resource Availability (RA)
The system is not paralyzed even by external attacks,
Ensures normal operation whenever needed
Identification and Authentication (IA)
Ensure that only authorized users have access to the system
Ability to verify and authenticate identity
Usage Control (UC)
Data accessible based on the user's role and permissions
Control functions to prevent unauthorized use
System Integrity (SI)
Protecting software and data from malware and hacking
Maintaining the integrity of the system by preventing forgery and tampering
Data Confidentiality (DC)
Encrypt important data such as patient sensitive information
Securely protected from unauthorized access and leaks
Timely Event Response (TRE)
Real-time security threat events such as hacking attempts
Support for detection, recording, and rapid response
Resource Availability (RA)
The system is not paralyzed even by external attacks,
Ensures normal operation whenever needed
Test procedure
application

Review and discussion of test standards

receipt

test

Issuance of test results





 KC
KC  FCC
FCC  ISED
ISED  CE
CE  UKCA
UKCA  TELEC, JATE
TELEC, JATE